第12节:new合约
小白入门:https://github.com/dukedaily/solidity-expert ,欢迎star转发,文末加V入群。
职场进阶: https://dukeweb3.com
创建合约时,在世界状态中,增加一个地址与账户的信息。
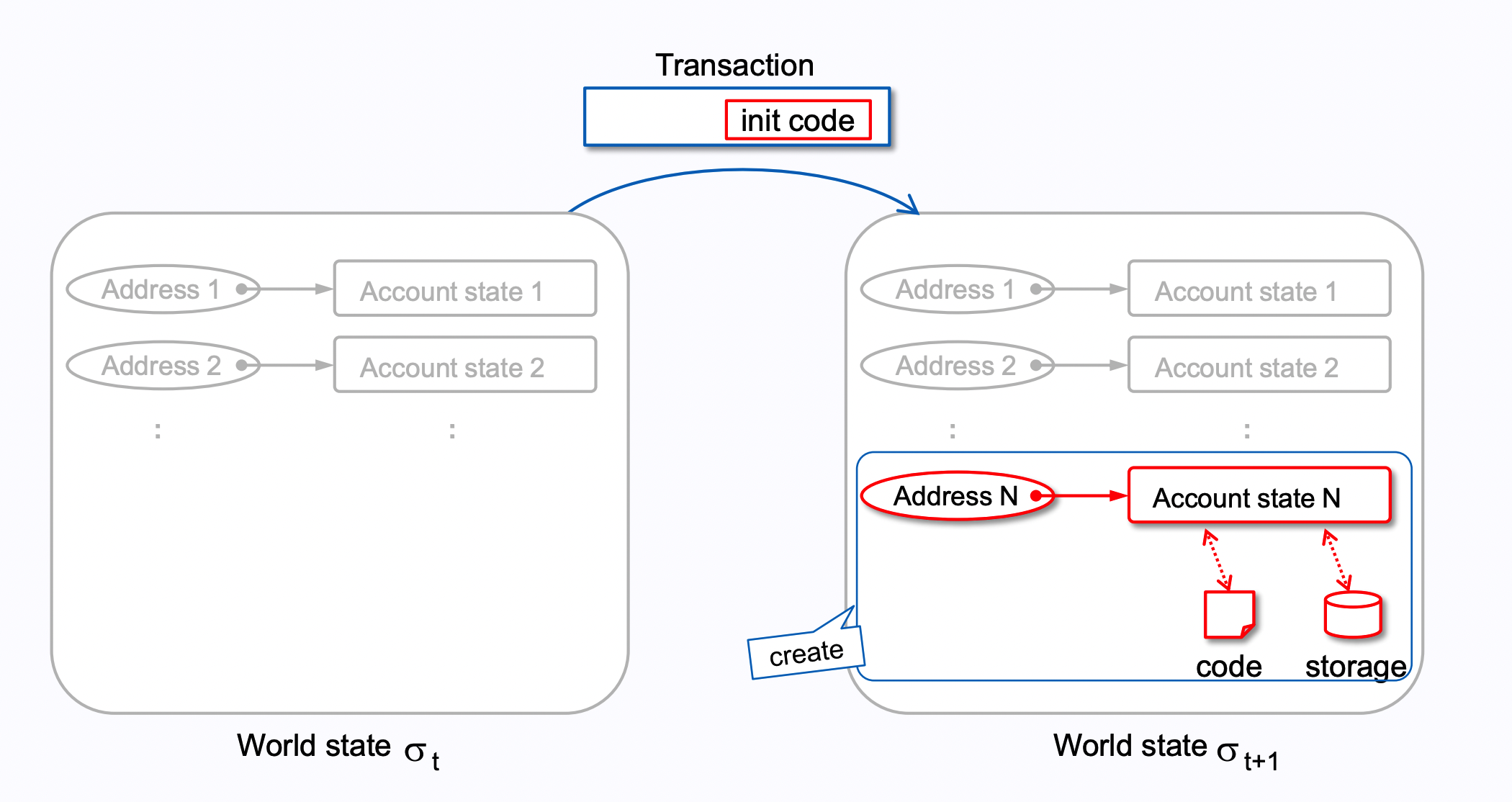
在EVM层面,一共有两个操作码(OPCODE)可以用来创建合约:
create:
原理:新生成地址 = hash(创建者地址, nonce)
特点:不可预测,因为nonce是变化的
create2:
原理:新生成地址 = hash("0xFF",创建者地址, salt, bytecodeHash)
- 特点:可以预测,因为没有变量
在编码时,我们可以直接使用汇编来创建新合约,也可以使用solidity中的new关键字来创建新合约:
- 使用汇编方式:
assembly {
create(参数...)
}
assembly {
create2(参数...)
}
- 使用new方式创建:
// 内部调用create
new ContractName(参数...)
// 内部调用create2
// 在0.8.0版本之后,new增加了salt选项,从而支持了create2的特性(通过salt可以计算出创建合约的地址)。
new ContractName{salt: _salt}(参数...)
demo验证
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
contract Car {
address public owner;
string public model;
address public carAddr;
constructor(address _owner, string memory _model) payable {
owner = _owner;
model = _model;
carAddr = address(this);
}
}
contract CarFactory {
Car[] public cars;
function create(address _owner, string memory _model) public {
Car car = new Car(_owner, _model);
cars.push(car);
}
function createAndSendEther(address _owner, string memory _model) public payable {
Car car = (new Car){value: msg.value}(_owner, _model);
cars.push(car);
}
function create2(
address _owner,
string memory _model,
bytes32 _salt
) public {
Car car = (new Car){salt: _salt}(_owner, _model);
cars.push(car);
}
function create2AndSendEther(
address _owner,
string memory _model,
bytes32 _salt
) public payable {
Car car = (new Car){value: msg.value, salt: _salt}(_owner, _model);
cars.push(car);
}
function getCar(uint _index)
public
view
returns (
address owner,
string memory model,
address carAddr,
uint balance
)
{
Car car = cars[_index];
return (car.owner(), car.model(), car.carAddr(), address(car).balance);
}
}